Filters
Host (770489)
Bovine (1090)Canine (20)Cat (408)Chicken (1642)Cod (2)Cow (333)Crab (15)Dog (524)Dolphin (2)Duck (13)E Coli (239125)Equine (7)Feline (1864)Ferret (306)Fish (125)Frog (55)Goat (36847)Guinea Pig (752)Hamster (1376)Horse (903)Insect (2053)Mammalian (512)Mice (6)Monkey (622)Mouse (96367)Pig (197)Porcine (70)Rabbit (360490)Rat (11713)Ray (55)Salamander (4)Salmon (15)Shark (3)Sheep (4247)Snake (4)Swine (301)Turkey (57)Whale (3)Yeast (5339)Zebrafish (3022)Isotype (157212)
IgA (13691)IgA1 (946)IgA2 (319)IgD (1964)IgE (5651)IgG (87493)IgG1 (16666)IgG2 (1330)IgG3 (2729)IgG4 (1695)IgM (22194)IgY (2534)Label (239657)
AF488 (2465)AF594 (662)AF647 (2324)ALEXA (11546)ALEXA FLUOR 350 (255)ALEXA FLUOR 405 (260)ALEXA FLUOR 488 (672)ALEXA FLUOR 532 (260)ALEXA FLUOR 555 (274)ALEXA FLUOR 568 (253)ALEXA FLUOR 594 (299)ALEXA FLUOR 633 (262)ALEXA FLUOR 647 (607)ALEXA FLUOR 660 (252)ALEXA FLUOR 680 (422)ALEXA FLUOR 700 (2)ALEXA FLUOR 750 (414)ALEXA FLUOR 790 (215)Alkaline Phosphatase (825)Allophycocyanin (32)ALP (387)AMCA (80)AP (1160)APC (15226)APC C750 (13)Apc Cy7 (1248)ATTO 390 (3)ATTO 488 (6)ATTO 550 (1)ATTO 594 (5)ATTO 647N (4)AVI (52)Beads (235)Beta Gal (2)BgG (1)BIMA (6)Biotin (27799)Biotinylated (1810)Blue (708)BSA (878)BTG (46)C Terminal (688)CF Blue (19)Colloidal (22)Conjugated (29282)Cy (163)Cy3 (390)Cy5 (2041)Cy5 5 (2469)Cy5 PE (1)Cy7 (3638)Dual (170)DY549 (3)DY649 (3)Dye (1)DyLight (1430)DyLight 405 (7)DyLight 488 (216)DyLight 549 (17)DyLight 594 (84)DyLight 649 (3)DyLight 650 (35)DyLight 680 (17)DyLight 800 (21)Fam (13)Fc Tag (8)FITC (30173)Flag (207)Fluorescent (146)GFP (580)GFP Tag (179)Glucose Oxidase (59)Gold (511)Green (580)GST (721)GST Tag (326)HA Tag (439)His (629)His Tag (504)Horseradish (550)HRP (12993)HSA (249)iFluor (16571)Isoform b (31)KLH (88)Luciferase (102)Magnetic (260)MBP (344)MBP Tag (93)Myc Tag (409)OC 515 (1)Orange (78)OVA (104)Pacific Blue (213)Particle (64)PE (33605)PerCP (8438)Peroxidase (1379)POD (11)Poly Hrp (94)Poly Hrp40 (13)Poly Hrp80 (3)Puro (32)Red (2440)RFP Tag (62)Rhodamine (607)RPE (910)S Tag (194)SCF (184)SPRD (351)Streptavidin (55)SureLight (77)T7 Tag (97)Tag (4800)Texas (1249)Texas Red (1231)Triple (10)TRITC (1401)TRX tag (90)Unconjugated (2106)Unlabeled (218)Yellow (84)Pathogen (489613)
Adenovirus (8687)AIV (317)Bordetella (25038)Borrelia (18284)Candida (17817)Chikungunya (639)Chlamydia (17666)CMV (121399)Coronavirus (5949)Coxsackie (859)Dengue (2872)EBV (1512)Echovirus (215)Enterovirus (677)Hantavirus (259)HAV (910)HBV (2098)HHV (876)HIV (7887)hMPV (302)HSV (2359)HTLV (635)Influenza (22155)Isolate (1208)KSHV (396)Lentivirus (3545)Lineage (3025)Lysate (127759)Marek (94)Measles (1169)Parainfluenza (1692)Poliovirus (3033)Poxvirus (81)Rabies (1530)Reovirus (536)Retrovirus (1069)Rhinovirus (511)Rotavirus (5358)RSV (1786)Rubella (1072)SIV (279)Strain (67791)Vaccinia (7231)VZV (667)WNV (369)Species (2989665)
Alligator (10)Bovine (159807)Canine (120802)Cat (13121)Chicken (113988)Cod (1)Cow (2031)Dog (12758)Dolphin (21)Duck (9606)Equine (2012)Feline (1019)Ferret (259)Fish (12875)Frog (1)Goat (90541)Guinea Pig (87959)Hamster (36959)Horse (41295)Human (958131)Insect (653)Lemur (119)Lizard (24)Monkey (110990)Mouse (471934)Pig (26233)Porcine (131969)Rabbit (127882)Rat (349252)Ray (443)Salmon (348)Seal (8)Shark (29)Sheep (105151)Snake (12)Swine (519)Toad (4)Turkey (244)Turtle (75)Whale (45)Zebrafish (535)Technique (5595867)
Activation (170412)Activity (10776)Affinity (44632)Agarose (2604)Aggregation (199)Antigen (135466)Apoptosis (27400)Array (2021)Blocking (71764)Blood (8529)Blot (10966)ChiP (814)Chromatin (6286)Colorimetric (9866)Control (80077)Culture (3219)Cytometry (5475)Depletion (56)DNA (172524)Dot (233)EIA (1039)Electron (6275)Electrophoresis (254)Elispot (1294)Enzymes (52762)Exosome (4280)Extract (1089)Fab (2229)FACS (43)FC (80588)Flow (6662)Fluorometric (1407)Formalin (97)Frozen (2669)Functional (707)Gel (2480)HTS (136)IF (12906)IHC (16566)Immunoassay (1589)Immunofluorescence (4119)Immunohistochemistry (72)Immunoprecipitation (68)intracellular (5602)IP (2854)iPSC (259)Isotype (8804)Lateral (1587)Lenti (319416)Light (37309)Microarray (47)MicroRNA (4835)Microscopy (52)miRNA (88042)Monoclonal (524774)Multi (3844)Multiplex (302)Negative (4255)PAGE (2521)Panel (1633)Paraffin (2587)PBS (20266)PCR (9)Peptide (276250)PerCP (13759)Polyclonal (2752395)Positive (6334)Precipitation (61)Premix (130)Primers (3464)Probe (2630)Profile (229)Pure (7818)Purification (15)Purified (78237)Real Time (3042)Resin (2975)Reverse (2438)RIA (460)RNAi (17)Rox (1023)RT PCR (6608)Sample (2666)SDS (1524)Section (2895)Separation (86)Sequencing (122)Shift (22)siRNA (319447)Standard (42464)Sterile (10168)Strip (1863)Taq (2)Tip (1172)Tissue (42843)Tube (3305)Vitro (3577)Vivo (980)WB (2515)Western Blot (10683)Tissue (2016611)
Adenocarcinoma (1075)Adipose (3463)Adrenal (657)Adult (4883)Amniotic (65)Animal (2453)Aorta (436)Appendix (89)Array (2021)Ascites (4737)Bile Duct (20)Bladder (1675)Blood (8529)Bone (27361)Brain (31212)Breast (10918)Calvaria (28)Carcinoma (13497)cDNA (58548)Cell (413580)Cellular (9348)Cerebellum (700)Cervix (232)Child (1)Choroid (19)Colon (3911)Connective (3602)Contaminant (3)Control (80077)Cord (661)Corpus (148)Cortex (698)Dendritic (1849)Diseased (265)Donor (1359)Duct (861)Duodenum (643)Embryo (425)Embryonic (4586)Endometrium (466)Endothelium (1424)Epidermis (166)Epithelium (4224)Esophagus (716)Exosome (4280)Eye (2033)Female (475)Frozen (2669)Gallbladder (155)Genital (5)Gland (3435)Granulocyte (8984)Heart (6851)Hela (408)Hippocampus (325)Histiocytic (74)Ileum (201)Insect (4880)Intestine (1945)Isolate (1208)Jejunum (175)Kidney (8079)Langerhans (283)Leukemia (21570)Liver (17342)Lobe (835)Lung (6074)Lymph (1208)Lymphatic (639)lymphocyte (22588)Lymphoma (12791)Lysate (127759)Lysosome (2813)Macrophage (31820)Male (1617)Malignant (1467)Mammary (1987)Mantle (1042)Marrow (2210)Mastocytoma (3)Matched (11710)Medulla (156)Melanoma (15525)Membrane (105788)Metastatic (3575)Mitochondrial (160328)Muscle (37425)Myeloma (748)Myocardium (11)Nerve (6399)Neuronal (17035)Node (1206)Normal (9486)Omentum (10)Ovarian (2511)Ovary (1173)Pair (47185)Pancreas (2843)Panel (1633)Penis (64)Peripheral (1910)Pharynx (122)Pituitary (5421)Placenta (4049)Prostate (9438)Proximal (318)Rectum (316)Region (202210)Retina (956)Salivary (3119)Sarcoma (6946)Section (2895)Serum (24915)Set (167649)Skeletal (13634)Skin (1882)Smooth (7574)Spinal (424)Spleen (2292)Stem (8898)Stomach (925)Stroma (49)Subcutaneous (47)Testis (15396)Thalamus (127)Thoracic (60)Throat (40)Thymus (2988)Thyroid (14149)Tongue (144)Total (10150)Trachea (227)Transformed (174)Tubule (48)Tumor (76982)Umbilical (208)Ureter (73)Urinary (2467)Uterine (303)Uterus (414)XRCC1 (X-ray Repair Cross-Complementing 1) and Its Genetic Silencing via shRNA Plasmid
Explore the XRCC1 Human shRNA Plasmid Kit (Locus ID 7515) for efficient XRCC1 gene silencing. Study DNA repair, SSBR/BER pathways and cell response to damage.
Genprice
Scientific Publications

XRCC1 (X-ray Repair Cross-Complementing 1) and Its Genetic Silencing via shRNA Plasmid
The human gene XRCC1
The human gene XRCC1(Wikipedia) (Gene ID 7515) encodes a scaffold protein central to single-strand break repair (SSBR) and base excision repair (BER). Impairments in XRCC1 function contribute to genomic instability, cancer susceptibility, aging phenotypes and neural degeneration. Effective silencing of XRCC1 via shRNA plasmid tools enables mechanistic studies of DNA-damage response (DDR), repair kinetics, synthetic lethality and phenotypic screening.
Image from ScienceDirecte : The article
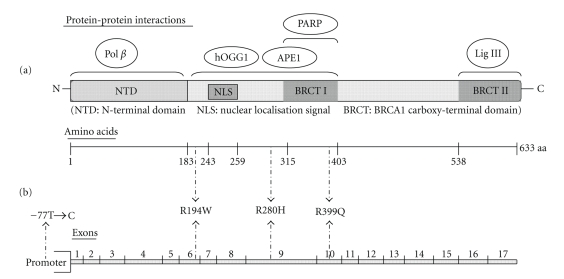
Gene Architecture and Molecular Role
According to the NCBI Gene database, XRCC1 is located on chromosome 19q13.31 in Homo sapiens (NCBI).The XRCC1 protein lacks catalytic activity; instead it acts as a scaffold recruiting DNA ligase IIIα, DNA polymerase β, PARP1/2, PNKP and other effectors to SSB sites.Structural analyses identify BRCT-type domains contributing to protein-protein interaction surfaces, linking XRCC1 to both SSBR and replication-associated break kinetics (GeneCards).
Photo from RsearchGate : The article
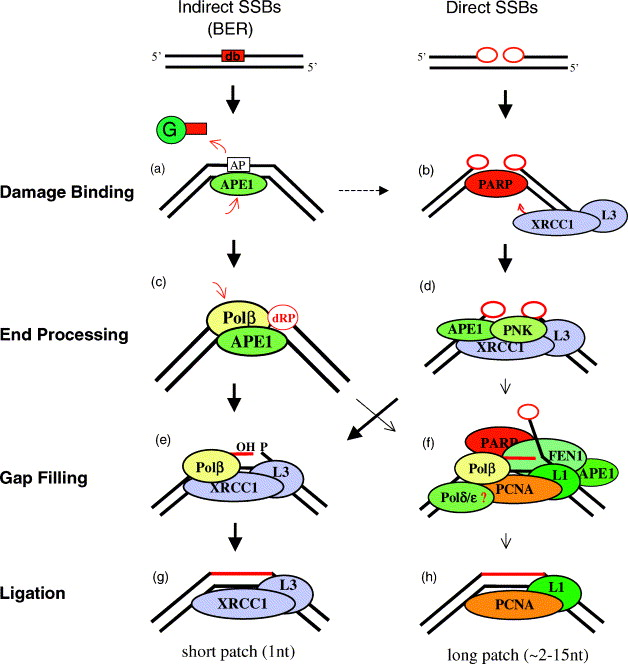
Biological Significance in SSBR/BER and Genome Stability
Single-strand breaks (SSBs) are common by-products of oxidative stress, replication fork collapse or alkylation damage. XRCC1, by orchestrating repair complex assembly, accelerates removal of abasic sites and SSB ends, thus maintaining genome integrity. When XRCC1 is deficient, unrepaired SSBs may become double-strand breaks (DSBs) during replication, increasing chromosomal aberrations and mutagenesis. This makes XRCC1 a vital node in DDR, aging research and cancer biology.
Single-strand breaks (SSBs) : ScienceDirecte
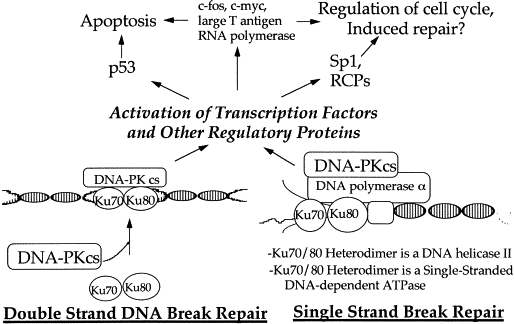
Research Targeting XRCC1
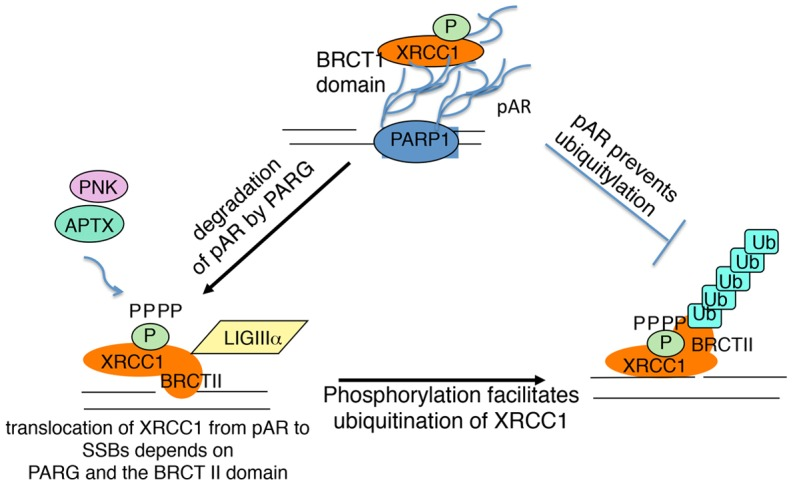
Because XRCC1 occupies a central position in repair pathways, silencing XRCC1 enables :
- Probing how SSBR/BER kinetics respond to knock-down and repair inhibitors.
- Evaluating synthetic-lethal interactions (e.g., combining XRCC1 knock-down with PARP inhibition).
- Modeling aging-related decline of repair capacity in stem cells or differentiated lineages.
- Investigating tumor-cell vulnerabilities to radiation/alkylating agents when XRCC1 is impaired.
A model of XRCC1-mediated repair of the SSB machinery : ResearchGate
Product Application : XRCC1 Human shRNA Plasmid Kit (Locus ID 7515)
The product page : XRCC1 Human shRNA Plasmid Kit (Locus ID 7515). This plasmid kit is designed to enable stable or transient knock-down of XRCC1 in human cell lines, facilitating functional genomic studies of repair mechanisms, genotoxic response assays, and phenotypic screens.
Key Features & Research Applications
- Human‐specific XRCC1 target (locus 7515), compatible with human cell lines.
- Vector backbone suitable for transfection or viral packaging (depending on your downstream workflow).
- Enables stable downstream assays (colony formation, γH2AX foci quantitation, sister‐chromatid exchange) after XRCC1 knock-down.
- Ideal for DDR (DNA damage response) research, repair inhibitor screening, aging/neurodegeneration models, and cancer research.
- Enhances reproducibility compared to siRNA by utilising plasmid-based knock-down for longer durations.
Experimental Considerations & Protocol Tips
-Cell line selection : Choose a human cell line with known baseline XRCC1 expression (e.g., fibroblasts, epithelial cancer lines). Confirm by Western blot or qPCR before knock-down.
-Transfection/Transduction : Depending on the plasmid, you may use lipid-based transfection or viral packaging. Optimize MOI or plasmid amount to minimise off-target toxicity.
-Knock-down validation : Use qPCR for XRCC1 mRNA and Western blot for XRCC1 protein levels. Confirm efficient knock-down (≥ 70 % reduction) before downstream assays.
-DNA-damage challenge : After knock-down, challenge cells with SSB-inducing agents (e.g., H₂O₂, camptothecin) or ionising radiation. Measure repair kinetics (γH2AX, 53BP1 foci clearance) and viability.
-Phenotypic read-out : Evaluate endpoints such as SCE (sister-chromatid exchange), chromosomal aberrations, comet assay for SSBs, cell cycle arrest, apoptosis. XRCC1 deficiency leads to elevated SCE and sensitivity to DNA-damage. ResearchGate
-Rescue experimen s : To confirm specificity, express an shRNA‐resistant XRCC1 cDNA and demonstrate phenotypic rescue (repair kinetics normalisation).
-Controls : Use scrambled/non-targeting shRNA plasmid, and ideally an unrelated DNA‐repair gene knock-down (e.g., XRCC3) as a comparative control.
-Downstream applications : Combine XRCC1 knock-down with chemical inhibitors (e.g., PARP inhibitors), or CRISPR destabilisation of other repair factors to probe synthetic-lethal interactions.
Why Targeting XRCC1 Matters in Research ?
Genomic Stability and Repair Pathway Cross-Talk
XRCC1 is integral to maintaining genomic stability by coordinating repair of single‐strand breaks (SSBs). Without efficient XRCC1 function, SSBs may convert to double-strand breaks (DSBs) during replication, elevating mutation rates and chromosomal aberrations. Additionally, XRCC1’s involvement extends into cross-talk with BER and PARP1 signalling. NCBI
Implications in Cancer Biology
Cells harboring XRCC1 deficiency or polymorphisms often display increased sensitivity to DNA-damaging therapies (radiation, alkylators).
On the other hand, over-expression of XRCC1 in some cancers may contribute to therapeutic resistance, making XRCC1 knock-down a strategy to potentiate DNA-damage based therapies.
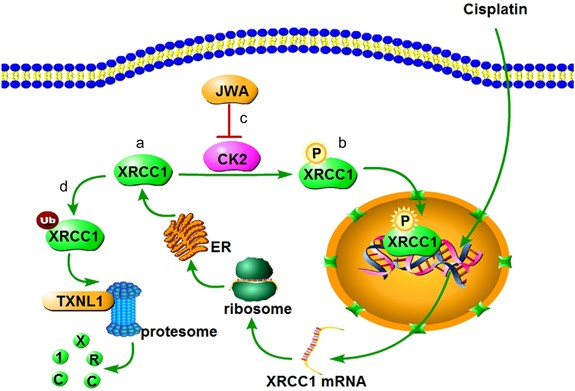
Neurodegeneration, Aging and Stem-Cell Studies
In aged human adipose-derived stem cells, BER capacity declines and XRCC1 has been shown to decline with age. Studies in muscle differentiation also show that XRCC1 activity is essential for timely myonuclear maturation (NBCI). Thus, XRCC1 knock-down models permit investigation into age-related repair decline, stem‐cell dysfunction, and differentiation-linked DNA damage responses.
The Xrcc1-deficient brain accumulates DNA damage in mature neurons
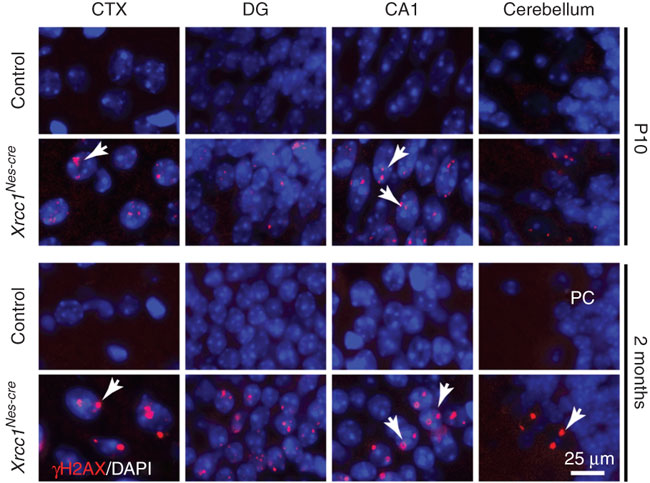
Using the XRCC1 Human shRNA Plasmid Kit for Functional Genomics of DNA Repair
The XRCC1 human shRNA plasmid kit is optimized for inducing stable or transient knock-down of XRCC1 in human cell lines. After transfection and confirmation of knock-down efficiency, cells may be challenged with ionising radiation, hydrogen peroxide or alkylators to trigger DNA single-strand breaks (SSBs). Because XRCC1 is a core scaffold in SSBR/BER, silencing XRCC1 leads to slower repair kinetics, elevated damage markers (e.g., γH2AX or 53BP1), increased sister-chromatid exchange and hypersensitivity to genotoxic stress. This makes it an ideal tool for investigations in genomic stability, aging, cancer and neurobiology.
Researchers may combine XRCC1 knock-down with chemical inhibition of PARP1 to explore synthetic-lethal interactions; for example, XRCC1 loss may potentiate PARP inhibitor sensitivity in certain cancer models. The plasmid kit also supports large‐scale screening, due to its plasmid format which allows selection of stable cell lines.
Tags
- XRCC1
- XRCC1 shRNA plasmid
- XRCC1 knock-down
- XRCC1 human plasmid kit
- XRCC1 cancer research tool
- DNA repair gene XRCC1
- SSBR BER XRCC1