Filters
Host (768597)
Bovine (1090)Canine (20)Cat (408)Chicken (1642)Cod (2)Cow (333)Crab (15)Dog (524)Dolphin (2)Duck (13)E Coli (239129)Equine (7)Feline (1864)Ferret (306)Fish (125)Frog (55)Goat (36847)Guinea Pig (752)Hamster (1376)Horse (903)Insect (2053)Mammalian (512)Mice (6)Monkey (601)Mouse (96266)Pig (197)Porcine (70)Rabbit (358709)Rat (11723)Ray (55)Salamander (4)Salmon (15)Shark (3)Sheep (4247)Snake (4)Swine (301)Turkey (57)Whale (3)Yeast (5336)Zebrafish (3022)Isotype (156643)
IgA (13624)IgA1 (941)IgA2 (318)IgD (1949)IgE (5594)IgG (87187)IgG1 (16733)IgG2 (1329)IgG3 (2719)IgG4 (1689)IgM (22029)IgY (2531)Label (239340)
AF488 (2465)AF594 (662)AF647 (2324)ALEXA (11546)ALEXA FLUOR 350 (255)ALEXA FLUOR 405 (260)ALEXA FLUOR 488 (672)ALEXA FLUOR 532 (260)ALEXA FLUOR 555 (274)ALEXA FLUOR 568 (253)ALEXA FLUOR 594 (299)ALEXA FLUOR 633 (262)ALEXA FLUOR 647 (607)ALEXA FLUOR 660 (252)ALEXA FLUOR 680 (422)ALEXA FLUOR 700 (2)ALEXA FLUOR 750 (414)ALEXA FLUOR 790 (215)Alkaline Phosphatase (825)Allophycocyanin (32)ALP (387)AMCA (80)AP (1160)APC (15217)APC C750 (13)Apc Cy7 (1248)ATTO 390 (3)ATTO 488 (6)ATTO 550 (1)ATTO 594 (5)ATTO 647N (4)AVI (53)Beads (225)Beta Gal (2)BgG (1)BIMA (6)Biotin (27817)Biotinylated (1810)Blue (708)BSA (878)BTG (46)C Terminal (688)CF Blue (19)Colloidal (22)Conjugated (29246)Cy (163)Cy3 (390)Cy5 (2041)Cy5 5 (2469)Cy5 PE (1)Cy7 (3638)Dual (170)DY549 (3)DY649 (3)Dye (1)DyLight (1430)DyLight 405 (7)DyLight 488 (216)DyLight 549 (17)DyLight 594 (84)DyLight 649 (3)DyLight 650 (35)DyLight 680 (17)DyLight 800 (21)Fam (5)Fc Tag (8)FITC (30165)Flag (208)Fluorescent (146)GFP (563)GFP Tag (164)Glucose Oxidase (59)Gold (511)Green (580)GST (711)GST Tag (315)HA Tag (430)His (619)His Tag (492)Horseradish (550)HRP (12960)HSA (249)iFluor (16571)Isoform b (31)KLH (88)Luciferase (105)Magnetic (254)MBP (338)MBP Tag (87)Myc Tag (398)OC 515 (1)Orange (78)OVA (104)Pacific Blue (213)Particle (64)PE (33571)PerCP (8438)Peroxidase (1380)POD (11)Poly Hrp (92)Poly Hrp40 (13)Poly Hrp80 (3)Puro (32)Red (2440)RFP Tag (63)Rhodamine (607)RPE (910)S Tag (194)SCF (184)SPRD (351)Streptavidin (55)SureLight (77)T7 Tag (97)Tag (4710)Texas (1249)Texas Red (1231)Triple (10)TRITC (1401)TRX tag (87)Unconjugated (2110)Unlabeled (218)Yellow (84)Pathogen (489613)
Adenovirus (8665)AIV (315)Bordetella (25035)Borrelia (18281)Candida (17817)Chikungunya (638)Chlamydia (17650)CMV (121394)Coronavirus (5948)Coxsackie (854)Dengue (2868)EBV (1510)Echovirus (215)Enterovirus (677)Hantavirus (254)HAV (905)HBV (2095)HHV (873)HIV (7865)hMPV (300)HSV (2356)HTLV (634)Influenza (22132)Isolate (1208)KSHV (396)Lentivirus (3755)Lineage (3025)Lysate (127759)Marek (93)Measles (1163)Parainfluenza (1681)Poliovirus (3030)Poxvirus (74)Rabies (1519)Reovirus (527)Retrovirus (1069)Rhinovirus (507)Rotavirus (5346)RSV (1781)Rubella (1070)SIV (277)Strain (67790)Vaccinia (7233)VZV (666)WNV (363)Species (2982223)
Alligator (10)Bovine (159546)Canine (120648)Cat (13082)Chicken (113771)Cod (1)Cow (2030)Dog (12745)Dolphin (21)Duck (9567)Equine (2004)Feline (996)Ferret (259)Fish (12797)Frog (1)Goat (90451)Guinea Pig (87888)Hamster (36959)Horse (41226)Human (955186)Insect (653)Lemur (119)Lizard (24)Monkey (110914)Mouse (470743)Pig (26204)Porcine (131703)Rabbit (127597)Rat (347841)Ray (442)Salmon (348)Seal (8)Shark (29)Sheep (104984)Snake (12)Swine (511)Toad (4)Turkey (244)Turtle (75)Whale (45)Zebrafish (535)Technique (5597646)
Activation (170393)Activity (10733)Affinity (44631)Agarose (2604)Aggregation (199)Antigen (135358)Apoptosis (27447)Array (2022)Blocking (71767)Blood (8528)Blot (10966)ChiP (815)Chromatin (6286)Colorimetric (9913)Control (80065)Culture (3218)Cytometry (5481)Depletion (54)DNA (172449)Dot (233)EIA (1039)Electron (6275)Electrophoresis (254)Elispot (1294)Enzymes (52671)Exosome (4280)Extract (1090)Fab (2230)FACS (43)FC (80929)Flow (6666)Fluorometric (1407)Formalin (97)Frozen (2671)Functional (708)Gel (2484)HTS (136)IF (12906)IHC (16566)Immunoassay (1589)Immunofluorescence (4119)Immunohistochemistry (72)Immunoprecipitation (68)intracellular (5602)IP (2840)iPSC (259)Isotype (8791)Lateral (1585)Lenti (319416)Light (37250)Microarray (47)MicroRNA (4834)Microscopy (52)miRNA (88044)Monoclonal (516109)Multi (3844)Multiplex (302)Negative (4261)PAGE (2520)Panel (1520)Paraffin (2587)PBS (20270)PCR (9)Peptide (276160)PerCP (13759)Polyclonal (2762994)Positive (6335)Precipitation (61)Premix (130)Primers (3467)Probe (2627)Profile (229)Pure (7808)Purification (15)Purified (78305)Real Time (3042)Resin (2955)Reverse (2435)RIA (460)RNAi (17)Rox (1022)RT PCR (6608)Sample (2667)SDS (1527)Section (2895)Separation (86)Sequencing (122)Shift (22)siRNA (319447)Standard (42468)Sterile (10170)Strip (1863)Taq (2)Tip (1176)Tissue (42812)Tube (3306)Vitro (3577)Vivo (981)WB (2515)Western Blot (10683)Tissue (2015946)
Adenocarcinoma (1075)Adipose (3459)Adrenal (657)Adult (4883)Amniotic (65)Animal (2447)Aorta (436)Appendix (89)Array (2022)Ascites (4377)Bile Duct (20)Bladder (1672)Blood (8528)Bone (27330)Brain (31189)Breast (10917)Calvaria (28)Carcinoma (13493)cDNA (58547)Cell (413805)Cellular (9357)Cerebellum (700)Cervix (232)Child (1)Choroid (19)Colon (3911)Connective (3601)Contaminant (3)Control (80065)Cord (661)Corpus (148)Cortex (698)Dendritic (1849)Diseased (265)Donor (1360)Duct (861)Duodenum (643)Embryo (425)Embryonic (4583)Endometrium (463)Endothelium (1424)Epidermis (166)Epithelium (4221)Esophagus (716)Exosome (4280)Eye (2033)Female (475)Frozen (2671)Gallbladder (155)Genital (5)Gland (3436)Granulocyte (8981)Heart (6850)Hela (413)Hippocampus (325)Histiocytic (74)Ileum (201)Insect (4880)Intestine (1944)Isolate (1208)Jejunum (175)Kidney (8075)Langerhans (283)Leukemia (21541)Liver (17340)Lobe (835)Lung (6064)Lymph (1208)Lymphatic (639)lymphocyte (22572)Lymphoma (12782)Lysate (127759)Lysosome (2813)Macrophage (31794)Male (1617)Malignant (1465)Mammary (1985)Mantle (1042)Marrow (2210)Mastocytoma (3)Matched (11710)Medulla (156)Melanoma (15522)Membrane (105772)Metastatic (3574)Mitochondrial (160319)Muscle (37419)Myeloma (748)Myocardium (11)Nerve (6398)Neuronal (17028)Node (1206)Normal (9486)Omentum (10)Ovarian (2509)Ovary (1172)Pair (47185)Pancreas (2843)Panel (1520)Penis (64)Peripheral (1912)Pharynx (122)Pituitary (5411)Placenta (4038)Prostate (9423)Proximal (318)Rectum (316)Region (202210)Retina (956)Salivary (3119)Sarcoma (6946)Section (2895)Serum (24880)Set (167654)Skeletal (13628)Skin (1879)Smooth (7577)Spinal (424)Spleen (2292)Stem (8892)Stomach (925)Stroma (49)Subcutaneous (47)Testis (15393)Thalamus (127)Thoracic (60)Throat (40)Thymus (2986)Thyroid (14121)Tongue (140)Total (10135)Trachea (227)Transformed (175)Tubule (48)Tumor (76921)Umbilical (208)Ureter (73)Urinary (2466)Uterine (303)Uterus (414)Understanding Four Common Neurological Diseases: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
This blog delves into the complexities of four common neurological diseases—Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Multiple Sclerosis, and Epilepsy. It explores their causes, symptoms, and available treatments to provide readers with an insightful overview of these conditions. Aimed at raising awareness, this blog is designed to help individuals better understand the impact of these diseases on the brain and nervous system, while also shedding light on current medical advancements in managing these disorders. Whether you're a patient, caregiver, or someone interested in neuroscience, this blog offers valuable information to navigate the challenges posed by neurological diseases.
Genprice
Scientific Publications
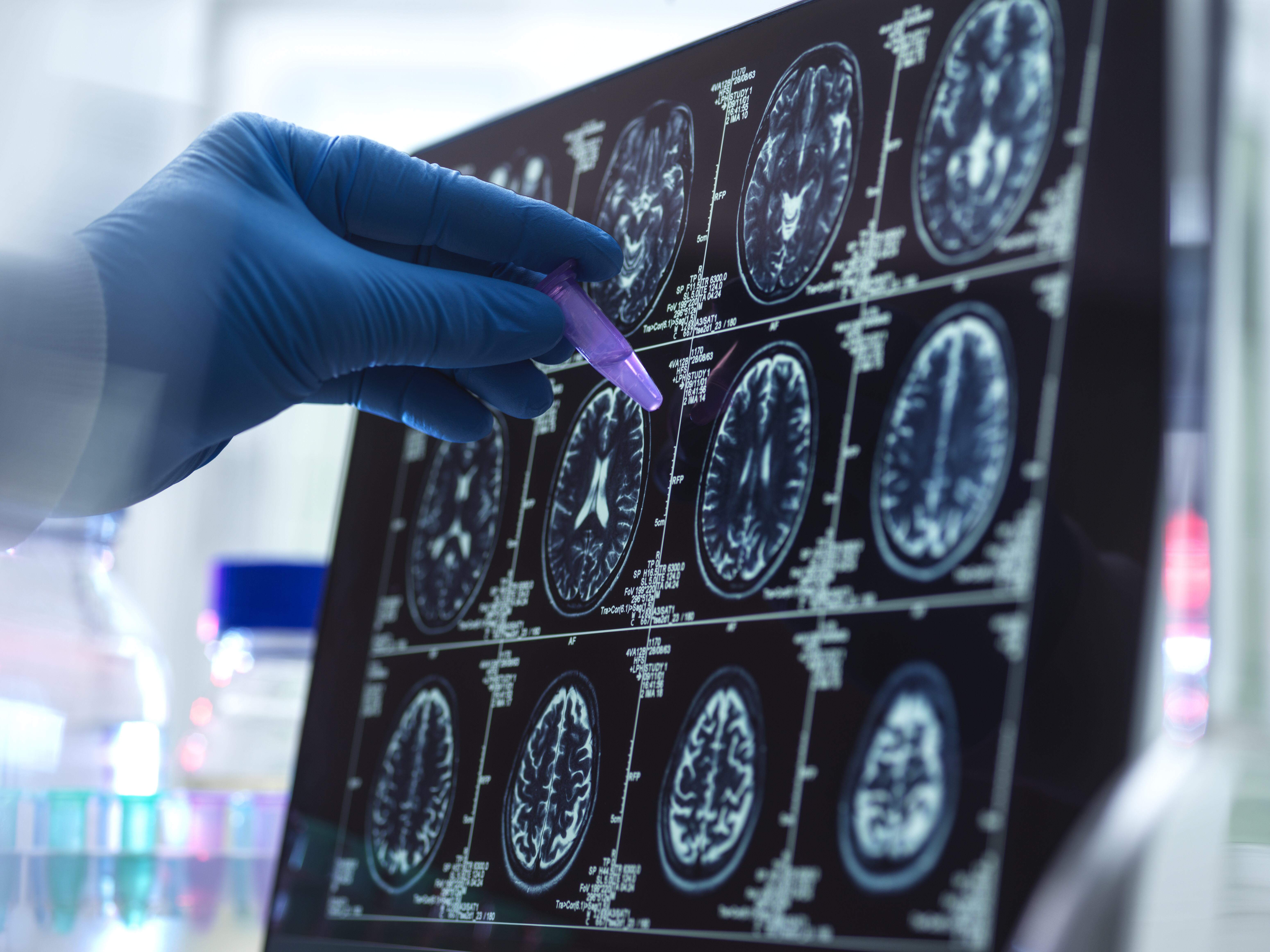
Understanding Four Common Neurological Diseases: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Introduction
Neurological diseases affect the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. These disorders can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, affecting movement, cognition, and even emotions. In this blog, we'll explore four common neurological diseases—Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis (MS), and epilepsy—highlighting their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Alzheimer's Disease: The Silent Decline
Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia, affecting millions worldwide. This progressive disease primarily impacts memory and cognitive function.
Causes:
While the exact cause remains unclear, Alzheimer's is linked to the accumulation of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain. Genetic factors and lifestyle choices like diet, exercise, and smoking can also contribute.
Symptoms:
- Memory loss
- Difficulty with language and communication
- Mood swings and personality changes
- Confusion about time and place
Treatment:
Currently, there is no cure for Alzheimer's, but medications like cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine can help manage symptoms. Lifestyle changes, including cognitive therapy and a brain-healthy diet, may slow progression.
Parkinson's Disease: A Movement Disorder
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects movement, leading to tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia (slowness of movement).
Causes:
Parkinson's is caused by the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain. While the exact cause is unknown, genetics, environmental factors, and age are known risk factors.
Symptoms:
- Tremors, especially in the hands
- Muscle stiffness
- Difficulty balancing and walking
- Speech and writing difficulties
Treatment:
There is no cure for Parkinson's, but medications like levodopa (a dopamine precursor) and dopamine agonists help manage symptoms. In some cases, deep brain stimulation (DBS) surgery may be recommended for severe cases.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS): The Immune System Attacks the Brain
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the protective covering (myelin) of nerve fibers in the brain and spinal cord.
Causes:
The exact cause of MS is unknown, but it's believed that a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors like viral infections can trigger the immune response.
Symptoms:
- Numbness or tingling in limbs
- Muscle weakness and coordination problems
- Vision problems (e.g., blurred or double vision)
- Fatigue and dizziness
Treatment:
There is no cure for MS, but treatments focus on managing symptoms and slowing disease progression. Disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) like interferons and oral medications can reduce relapses. Steroid treatments are used to manage flare-ups.
Epilepsy: Unpredictable Seizures
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurring seizures, which occur due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
Causes:
Epilepsy can result from brain injuries, genetic factors, infections, or developmental disorders. In some cases, the cause is unknown.
Symptoms:
- Uncontrolled jerking movements
- Temporary confusion
- Loss of consciousness
- Aura (a sensation before a seizure, like a strange smell or visual disturbance)
Treatment:
Epilepsy is typically managed with antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). For those who do not respond to medication, surgical options like resecting the area of the brain causing seizures or implanting a Vagus Nerve Stimulator (VNS) may be considered.
Conclusion: Living with Neurological Diseases
Living with neurological diseases can be challenging, both for those affected and their families. Although there is no universal cure for these conditions, advances in research and treatment options continue to improve the lives of patients. If you or someone you know is struggling with a neurological disorder, seeking medical guidance and treatment early can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
