Filters
Host (772561)
Bovine (1090)Canine (20)Cat (403)Chicken (1642)Cod (2)Cow (333)Crab (15)Dog (524)Dolphin (2)Duck (13)E Coli (239133)Equine (7)Feline (1866)Ferret (306)Fish (125)Frog (52)Goat (37446)Guinea Pig (752)Hamster (1376)Horse (903)Insect (2054)Mammalian (512)Mice (6)Monkey (624)Mouse (96940)Pig (197)Porcine (70)Rabbit (361350)Rat (11751)Ray (55)Salamander (4)Salmon (15)Shark (3)Sheep (4248)Snake (4)Swine (301)Turkey (57)Whale (3)Yeast (5335)Zebrafish (3022)Isotype (157740)
IgA (13452)IgA1 (913)IgA2 (309)IgD (1984)IgE (5456)IgG (88060)IgG1 (16838)IgG2 (1325)IgG3 (2725)IgG4 (1694)IgM (22253)IgY (2731)Label (241822)
AF488 (2868)AF594 (719)AF647 (2711)ALEXA (12104)ALEXA FLUOR 350 (298)ALEXA FLUOR 405 (303)ALEXA FLUOR 488 (715)ALEXA FLUOR 532 (303)ALEXA FLUOR 555 (317)ALEXA FLUOR 568 (296)ALEXA FLUOR 594 (342)ALEXA FLUOR 633 (305)ALEXA FLUOR 647 (650)ALEXA FLUOR 660 (295)ALEXA FLUOR 680 (465)ALEXA FLUOR 700 (2)ALEXA FLUOR 750 (457)ALEXA FLUOR 790 (258)Alkaline Phosphatase (825)Allophycocyanin (32)ALP (387)AMCA (133)AP (1213)APC (14722)APC C750 (13)Apc Cy7 (1248)ATTO 390 (3)ATTO 488 (6)ATTO 550 (1)ATTO 594 (5)ATTO 647N (4)AVI (53)Beads (235)Beta Gal (2)BgG (1)BIMA (6)Biotin (27912)Biotinylated (1810)Blue (708)BSA (878)BTG (46)C Terminal (688)CF Blue (19)Colloidal (22)Conjugated (29545)Cy (163)Cy3 (445)Cy5 (2092)Cy5 5 (2520)Cy5 PE (1)Cy7 (3689)Dual (170)DY549 (3)DY649 (3)Dye (1)DyLight (1459)DyLight 405 (11)DyLight 488 (223)DyLight 549 (22)DyLight 594 (90)DyLight 649 (4)DyLight 650 (35)DyLight 680 (20)DyLight 800 (24)Fam (13)Fc Tag (8)FITC (29672)Flag (223)Fluorescent (146)GFP (576)GFP Tag (180)Glucose Oxidase (59)Gold (511)Green (580)GST (722)GST Tag (327)HA Tag (455)His (649)His Tag (522)Horseradish (550)HRP (13090)HSA (247)iFluor (16571)Isoform b (31)KLH (87)Luciferase (105)Magnetic (260)MBP (343)MBP Tag (93)Myc Tag (425)OC 515 (1)Orange (78)OVA (103)Pacific Blue (213)Particle (64)PE (34110)PerCP (7934)Peroxidase (1364)POD (11)Poly Hrp (94)Poly Hrp40 (13)Poly Hrp80 (3)Puro (32)Red (2491)RFP Tag (63)Rhodamine (612)RPE (910)S Tag (194)SCF (184)SPRD (351)Streptavidin (55)SureLight (77)T7 Tag (97)Tag (4866)Texas (1300)Texas Red (1282)Triple (10)TRITC (1457)TRX tag (90)Unconjugated (2116)Unlabeled (218)Yellow (84)Pathogen (489316)
Adenovirus (8667)AIV (317)Bordetella (25037)Borrelia (18285)Candida (17801)Chikungunya (641)Chlamydia (17580)CMV (121402)Coronavirus (5969)Coxsackie (857)Dengue (2875)EBV (1485)Echovirus (215)Enterovirus (677)Hantavirus (260)HAV (909)HBV (2084)HHV (838)HIV (7877)hMPV (275)HSV (2335)HTLV (635)Influenza (22008)Isolate (1208)KSHV (396)Lentivirus (3755)Lineage (2930)Lysate (127759)Marek (95)Measles (1170)Parainfluenza (1692)Poliovirus (3025)Poxvirus (82)Rabies (1528)Reovirus (538)Retrovirus (1066)Rhinovirus (512)Rotavirus (5356)RSV (1768)Rubella (1070)SIV (279)Strain (67791)Vaccinia (7236)VZV (661)WNV (370)Species (2846114)
Alligator (10)Bovine (150365)Canine (112050)Cat (13087)Chicken (105007)Cod (1)Cow (2031)Dog (12177)Dolphin (21)Duck (9730)Equine (2088)Feline (1019)Ferret (259)Fish (12812)Frog (1)Goat (81633)Guinea Pig (79035)Hamster (36722)Horse (41046)Human (926494)Insect (653)Lemur (117)Lizard (24)Monkey (102155)Mouse (457050)Pig (25299)Porcine (123396)Rabbit (118469)Rat (334960)Ray (435)Salmon (344)Seal (8)Shark (29)Sheep (96163)Snake (11)Swine (519)Toad (4)Turkey (244)Turtle (75)Whale (45)Zebrafish (526)Technique (11565133)
Activation (211810)Activity (15308)Affinity (89553)Agarose (3204)Aggregation (229)Antigen (171903)Apoptosis (28531)Array (3334)Blocking (105044)Blood (10609)Blot (15167)ChiP (1046)Chromatin (6182)Colorimetric (14481)Control (90313)Culture (5592)Cytometry (5669)Depletion (122)DNA (182951)Dot (315)EIA (1082)Electron (6379)Electrophoresis (438)ELISA (2941926)Elispot (2324)Enzymes (55898)Exosome (4924)Extract (1464)Fab (3119)FACS (61)FC (98236)Filter Tips (388)Flow (14262)Fluorometric (1559)Formalin (122)Frozen (22754)Functional (731)Gel (3362)HTS (174)IF (12303)IHC (27118)Immunoassay (8462)Immunofluorescence (5625)Immunohistochemistry (81)Immunoprecipitation (80)intracellular (5786)IP (4366)iPSC (342)Isotype (17654)Lateral (1806)Lenti (382497)Light (44857)Microarray (203)MicroRNA (4886)Microscopy (808)miRNA (134352)Monoclonal (1478959)Multi (5178)Multiplex (7702)Negative (4547)PAGE (2639)Panel (2360)Paraffin (2732)PBS (27864)PCR (9)Peptide (335477)PerCP (67522)Polyclonal (3798314)Positive (6592)Precipitation (84)Premix (155)Primers (47311)Probe (3175)Profile (561)Pure (10551)Purification (15)Purified (111252)Real Time (3379)Resin (3256)Reverse (3102)RIA (521)RNAi (63116)Rox (1339)RT PCR (6831)Sample (4733)SDS (1885)Section (2971)Separation (246)Sequencing (222)Shift (21)siRNA (587501)Standard (74021)Sterile (11993)Strip (2479)Taq (2)Tip (1721)Tissue (83184)Tube (4397)Vitro (3588)Vivo (2366)WB (3025)Western Blot (14443)Tissue (2000497)
Adenocarcinoma (1075)Adipose (3370)Adrenal (645)Adult (4877)Amniotic (65)Animal (2451)Aorta (436)Appendix (89)Array (2022)Ascites (4737)Bile Duct (20)Bladder (1637)Blood (8473)Bone (26827)Brain (30653)Breast (10787)Calvaria (28)Carcinoma (13359)cDNA (58549)Cell (409997)Cellular (9283)Cerebellum (700)Cervix (232)Child (1)Choroid (19)Colon (3856)Connective (3543)Contaminant (3)Control (80435)Cord (661)Corpus (148)Cortex (686)Dendritic (1825)Diseased (265)Donor (1360)Duct (820)Duodenum (641)Embryo (425)Embryonic (4559)Endometrium (454)Endothelium (1426)Epidermis (166)Epithelium (4152)Esophagus (717)Exosome (4279)Eye (1943)Female (475)Frozen (2671)Gallbladder (155)Genital (5)Gland (3400)Granulocyte (8802)Heart (6804)Hela (413)Hippocampus (325)Histiocytic (74)Ileum (201)Insect (4881)Intestine (1945)Isolate (1208)Jejunum (175)Kidney (7988)Langerhans (283)Leukemia (21382)Liver (17120)Lobe (819)Lung (6010)Lymph (1208)Lymphatic (637)lymphocyte (22364)Lymphoma (12590)Lysate (127759)Lysosome (2774)Macrophage (31456)Male (1605)Malignant (1448)Mammary (1959)Mantle (1042)Marrow (2182)Mastocytoma (3)Matched (11710)Medulla (156)Melanoma (15346)Membrane (105024)Metastatic (3588)Mitochondrial (156751)Muscle (37036)Myeloma (748)Myocardium (11)Nerve (6310)Neuronal (16782)Node (1206)Normal (9456)Omentum (10)Ovarian (2476)Ovary (1157)Pair (47185)Pancreas (2814)Panel (1633)Penis (64)Peripheral (1902)Pharynx (122)Pituitary (5329)Placenta (4001)Prostate (9345)Proximal (318)Rectum (316)Region (201782)Retina (956)Salivary (3075)Sarcoma (6933)Section (2895)Serum (24684)Set (167576)Skeletal (13476)Skin (1852)Smooth (7511)Spinal (424)Spleen (2269)Stem (8826)Stomach (922)Stroma (49)Subcutaneous (47)Testis (15232)Thalamus (127)Thoracic (60)Throat (42)Thymus (2941)Thyroid (13823)Tongue (144)Total (9935)Trachea (227)Transformed (175)Tubule (48)Tumor (76117)Umbilical (208)Ureter (73)Urinary (2413)Cell Sorting Techniques: An In-Depth Look at FACS Technology
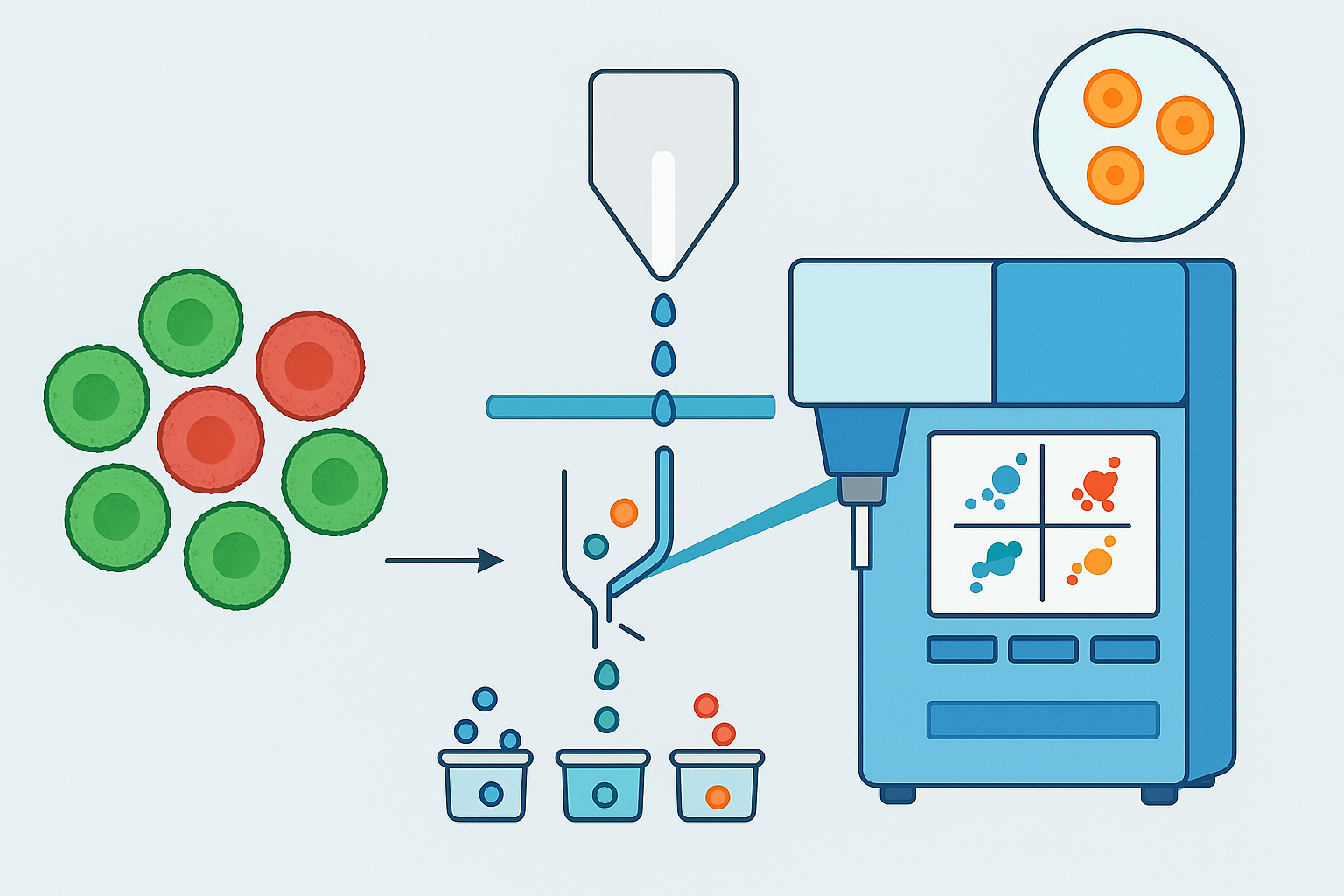
Cell sorting is a critical process in molecular biology, immunology, and biomedical research, enabling scientists to separate and analyze individual cells based on their characteristics. One of the most widely used and effective techniques for cell sorting is Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS). FACS has revolutionized how researchers can isolate and study cells, offering precision and flexibility in sorting heterogeneous cell populations. This blog dives into the principles, applications, and recent advancements in FACS technology.
Genprice
Scientific Publications
Cell Sorting Techniques: An In-Depth Look at FACS Technology
What is FACS (Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting)?
Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) is a sophisticated laboratory technique that allows the rapid and accurate isolation of specific cells from a heterogeneous mixture based on their fluorescence characteristics. The process involves labeling cells with fluorescent markers that bind to cell-specific proteins or markers. These fluorescently labeled cells are then passed through a laser beam in the flow cytometer, where they are sorted and collected based on their unique fluorescence signals.
FACS systems rely on a combination of flow cytometry and fluorescent labeling to distinguish between cells of different types, sizes, or states. The flow cytometer detects the light emitted by these labels and sorts the cells according to specific parameters such as size, complexity, or surface markers.
How Does FACS Work?
The process of FACS involves several key steps:
- Sample Preparation: Cells are prepared by suspending them in a liquid medium and staining them with fluorescently labeled antibodies or other molecular probes. These markers are designed to target specific cell types or biomarkers.
- Flow Cytometry: The prepared sample is injected into the flow cytometer, where individual cells flow through a laser beam. Each cell’s physical and fluorescent properties are analyzed as they pass through the beam.
- Light Detection: As the cells pass through the laser, they scatter light, and the detectors measure this light. The fluorescence emitted by the dyes on the cells is also recorded, providing detailed information about the cellular characteristics.
- Sorting: Based on the measured parameters (e.g., fluorescence, cell size), the cells are sorted into different groups using an electrostatic charge. This process can isolate a specific population of cells for further analysis.
Applications of FACS
FACS technology has numerous applications in research and clinical laboratories. Some of the major applications include:
- Immunology: FACS is widely used to identify and isolate different immune cell populations such as T-cells, B-cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages. By sorting these cells, researchers can study their functions, interactions, and roles in immune responses.
- Stem Cell Research: FACS is invaluable in isolating specific stem cell populations from a mixed sample. This is critical for studying stem cell differentiation and development, as well as for therapeutic applications.
- Cancer Research: FACS is used to isolate and characterize tumor cells from blood or tissue samples. By sorting cancerous cells from healthy cells, scientists can gain insights into tumor heterogeneity, genetic mutations, and potential therapeutic targets.
- Gene Expression Analysis: FACS can isolate cells based on the expression of specific genes or proteins. This allows researchers to study gene expression patterns in specific cell types or under various experimental conditions.
- Microbial Analysis: FACS has been used to sort and analyze microbial populations in environmental and clinical samples. It provides a rapid and efficient method for isolating microorganisms based on their specific fluorescence signatures.
- Cell Therapy and Transplantation: In cell-based therapies, FACS is used to isolate specific cell types for transplantation or to monitor the quality and purity of cell preparations.
Click here for an overview about Flow Cytometry
Recent Advancements in FACS Technology
FACS technology has evolved significantly over the years, with advancements improving its resolution, speed, and versatility. Some of the recent innovations include:
- Multi-Parameter FACS: Modern FACS systems can analyze many more parameters simultaneously, using an expanded range of fluorescent dyes. This enables the analysis of multiple cell markers in a single experiment, providing a deeper understanding of cell populations.
- High-Speed Sorting: Newer FACS systems offer high-speed sorting, capable of processing thousands of cells per second. This is essential for applications requiring the sorting of rare or high-throughput cell populations.
- Single-Cell Analysis: With the growing focus on single-cell genomics, FACS technology has advanced to facilitate the sorting of individual cells for downstream sequencing and analysis. This has become a crucial tool for understanding cellular heterogeneity and the complex behavior of single cells within tissues.
- Tandem Dyes and Spectral Flow Cytometry: New innovations in tandem dyes and spectral flow cytometry allow for more complex, multi-dimensional analysis of cell populations, improving the accuracy of cell sorting and expanding its capabilities for complex applications.
Conclusion
Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) is an indispensable tool in modern biomedical research. With its high precision, versatility, and ability to sort large numbers of cells based on specific characteristics, it has become a cornerstone of research in immunology, cancer biology, stem cell research, and many other fields. As the technology continues to evolve, FACS is poised to further enhance our understanding of cellular function and improve the development of targeted therapies and diagnostics.
For researchers seeking to dive deeper into FACS applications or explore its integration into their studies, continued innovation in flow cytometry and related technologies offers even greater promise in advancing cellular research.
