Filters
Host (768596)
Bovine (1090)Canine (20)Cat (408)Chicken (1642)Cod (2)Cow (333)Crab (15)Dog (524)Dolphin (2)Duck (13)E Coli (239125)Equine (7)Feline (1864)Ferret (306)Fish (125)Frog (55)Goat (36847)Guinea Pig (752)Hamster (1376)Horse (903)Insect (2053)Mammalian (512)Mice (6)Monkey (601)Mouse (96271)Pig (197)Porcine (70)Rabbit (358707)Rat (11723)Ray (55)Salamander (4)Salmon (15)Shark (3)Sheep (4247)Snake (4)Swine (301)Turkey (57)Whale (3)Yeast (5336)Zebrafish (3022)Isotype (157040)
IgA (13675)IgA1 (943)IgA2 (319)IgD (1949)IgE (5625)IgG (87443)IgG1 (16651)IgG2 (1330)IgG3 (2720)IgG4 (1689)IgM (22162)IgY (2534)Label (239268)
AF488 (2465)AF594 (662)AF647 (2324)ALEXA (11546)ALEXA FLUOR 350 (255)ALEXA FLUOR 405 (260)ALEXA FLUOR 488 (672)ALEXA FLUOR 532 (260)ALEXA FLUOR 555 (274)ALEXA FLUOR 568 (253)ALEXA FLUOR 594 (299)ALEXA FLUOR 633 (262)ALEXA FLUOR 647 (607)ALEXA FLUOR 660 (252)ALEXA FLUOR 680 (422)ALEXA FLUOR 700 (2)ALEXA FLUOR 750 (414)ALEXA FLUOR 790 (215)Alkaline Phosphatase (825)Allophycocyanin (32)ALP (387)AMCA (80)AP (1160)APC (15217)APC C750 (13)Apc Cy7 (1248)ATTO 390 (3)ATTO 488 (6)ATTO 550 (1)ATTO 594 (5)ATTO 647N (4)AVI (52)Beads (225)Beta Gal (2)BgG (1)BIMA (6)Biotin (27799)Biotinylated (1810)Blue (708)BSA (878)BTG (46)C Terminal (688)CF Blue (19)Colloidal (22)Conjugated (29246)Cy (163)Cy3 (390)Cy5 (2041)Cy5 5 (2469)Cy5 PE (1)Cy7 (3638)Dual (170)DY549 (3)DY649 (3)Dye (1)DyLight (1430)DyLight 405 (7)DyLight 488 (216)DyLight 549 (17)DyLight 594 (84)DyLight 649 (3)DyLight 650 (35)DyLight 680 (17)DyLight 800 (21)Fam (5)Fc Tag (8)FITC (30165)Flag (207)Fluorescent (146)GFP (562)GFP Tag (163)Glucose Oxidase (59)Gold (511)Green (580)GST (709)GST Tag (314)HA Tag (429)His (614)His Tag (489)Horseradish (550)HRP (12959)HSA (249)iFluor (16571)Isoform b (31)KLH (88)Luciferase (102)Magnetic (254)MBP (338)MBP Tag (87)Myc Tag (397)OC 515 (1)Orange (78)OVA (104)Pacific Blue (213)Particle (64)PE (33555)PerCP (8438)Peroxidase (1380)POD (11)Poly Hrp (92)Poly Hrp40 (13)Poly Hrp80 (3)Puro (32)Red (2440)RFP Tag (62)Rhodamine (607)RPE (910)S Tag (194)SCF (184)SPRD (351)Streptavidin (55)SureLight (77)T7 Tag (97)Tag (4698)Texas (1249)Texas Red (1231)Triple (10)TRITC (1401)TRX tag (87)Unconjugated (2106)Unlabeled (218)Yellow (84)Pathogen (489584)
Adenovirus (8685)AIV (317)Bordetella (25038)Borrelia (18284)Candida (17817)Chikungunya (639)Chlamydia (17666)CMV (121399)Coronavirus (5949)Coxsackie (859)Dengue (2872)EBV (1512)Echovirus (215)Enterovirus (677)Hantavirus (259)HAV (907)HBV (2098)HHV (876)HIV (7866)hMPV (302)HSV (2357)HTLV (635)Influenza (22155)Isolate (1208)KSHV (396)Lentivirus (3545)Lineage (3025)Lysate (127759)Marek (94)Measles (1169)Parainfluenza (1692)Poliovirus (3033)Poxvirus (81)Rabies (1530)Reovirus (536)Retrovirus (1069)Rhinovirus (511)Rotavirus (5358)RSV (1786)Rubella (1071)SIV (279)Strain (67791)Vaccinia (7231)VZV (667)WNV (369)Species (2987986)
Alligator (10)Bovine (159807)Canine (120802)Cat (13115)Chicken (113988)Cod (1)Cow (2031)Dog (12746)Dolphin (21)Duck (9606)Equine (2012)Feline (1019)Ferret (259)Fish (12875)Frog (1)Goat (90540)Guinea Pig (87959)Hamster (36959)Horse (41295)Human (956851)Insect (653)Lemur (119)Lizard (24)Monkey (110966)Mouse (471610)Pig (26206)Porcine (131969)Rabbit (127881)Rat (349250)Ray (443)Salmon (348)Seal (8)Shark (29)Sheep (105151)Snake (12)Swine (517)Toad (4)Turkey (244)Turtle (75)Whale (45)Zebrafish (535)Technique (5617788)
Activation (170406)Activity (10783)Affinity (44630)Agarose (2604)Aggregation (199)Antigen (135454)Apoptosis (27470)Array (2021)Blocking (71764)Blood (8531)Blot (10966)ChiP (815)Chromatin (6286)Colorimetric (9872)Control (80058)Culture (3218)Cytometry (5481)Depletion (54)DNA (172471)Dot (233)EIA (1039)Electron (6275)Electrophoresis (254)Elispot (1294)Enzymes (52752)Exosome (4280)Extract (1089)Fab (2229)FACS (43)FC (80500)Flow (6666)Fluorometric (1407)Formalin (97)Frozen (2669)Functional (707)Gel (2484)HTS (136)IF (12906)IHC (16566)Immunoassay (1589)Immunofluorescence (4119)Immunohistochemistry (72)Immunoprecipitation (68)intracellular (5602)IP (2840)iPSC (259)Isotype (8791)Lateral (1585)Lenti (319416)Light (37260)Microarray (47)MicroRNA (4835)Microscopy (52)miRNA (88044)Monoclonal (517524)Multi (3844)Multiplex (302)Negative (4255)PAGE (2521)Panel (1520)Paraffin (2587)PBS (20270)PCR (9)Peptide (276231)PerCP (13759)Polyclonal (2781816)Positive (6334)Precipitation (61)Premix (130)Primers (3464)Probe (2627)Profile (229)Pure (7808)Purification (15)Purified (78306)Real Time (3042)Resin (2955)Reverse (2436)RIA (460)RNAi (17)Rox (1022)RT PCR (6608)Sample (2667)SDS (1528)Section (2895)Separation (86)Sequencing (122)Shift (22)siRNA (319447)Standard (42467)Sterile (10171)Strip (1863)Taq (2)Tip (1176)Tissue (42842)Tube (3305)Vitro (3577)Vivo (980)WB (2515)Western Blot (10683)Tissue (2016418)
Adenocarcinoma (1075)Adipose (3463)Adrenal (657)Adult (4883)Amniotic (65)Animal (2447)Aorta (436)Appendix (89)Array (2021)Ascites (4737)Bile Duct (20)Bladder (1675)Blood (8531)Bone (27361)Brain (31207)Breast (10918)Calvaria (28)Carcinoma (13496)cDNA (58547)Cell (413564)Cellular (9348)Cerebellum (700)Cervix (232)Child (1)Choroid (19)Colon (3911)Connective (3602)Contaminant (3)Control (80058)Cord (661)Corpus (148)Cortex (698)Dendritic (1849)Diseased (265)Donor (1359)Duct (861)Duodenum (643)Embryo (425)Embryonic (4586)Endometrium (466)Endothelium (1424)Epidermis (166)Epithelium (4224)Esophagus (716)Exosome (4280)Eye (2033)Female (475)Frozen (2669)Gallbladder (155)Genital (5)Gland (3435)Granulocyte (8984)Heart (6851)Hela (408)Hippocampus (325)Histiocytic (74)Ileum (201)Insect (4880)Intestine (1945)Isolate (1208)Jejunum (175)Kidney (8079)Langerhans (283)Leukemia (21555)Liver (17346)Lobe (835)Lung (6064)Lymph (1208)Lymphatic (639)lymphocyte (22588)Lymphoma (12791)Lysate (127759)Lysosome (2813)Macrophage (31815)Male (1617)Malignant (1467)Mammary (1987)Mantle (1042)Marrow (2210)Mastocytoma (3)Matched (11710)Medulla (156)Melanoma (15525)Membrane (105788)Metastatic (3575)Mitochondrial (160328)Muscle (37432)Myeloma (748)Myocardium (11)Nerve (6399)Neuronal (17035)Node (1206)Normal (9486)Omentum (10)Ovarian (2511)Ovary (1173)Pair (47185)Pancreas (2843)Panel (1520)Penis (64)Peripheral (1910)Pharynx (122)Pituitary (5415)Placenta (4040)Prostate (9433)Proximal (318)Rectum (316)Region (202210)Retina (956)Salivary (3119)Sarcoma (6946)Section (2895)Serum (24906)Set (167658)Skeletal (13634)Skin (1882)Smooth (7581)Spinal (424)Spleen (2292)Stem (8893)Stomach (925)Stroma (49)Subcutaneous (47)Testis (15393)Thalamus (127)Thoracic (60)Throat (40)Thymus (2988)Thyroid (14147)Tongue (144)Total (10158)Trachea (227)Transformed (174)Tubule (48)Tumor (76982)Umbilical (208)Ureter (73)Urinary (2467)Uterine (303)Uterus (414)Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cell Therapy: A Revolution in Cancer Treatment
In recent years, cancer treatment has entered a new era, driven by groundbreaking advancements in immunotherapy. At the forefront of this revolution is Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy—a cutting-edge approach that reprograms the body’s own immune cells to recognize and attack cancer. Unlike traditional treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation, CAR T-cell therapy offers a highly personalized and targeted strategy, especially for patients with hard-to-treat or relapsed cancers. In this blog, we’ll explore how CAR T-cell therapy works, its proven success in blood cancers, potential applications in solid tumors, and why it’s become one of the most talked-about innovations in modern medicine. Whether you're a healthcare professional, researcher, patient, or biotech enthusiast, this comprehensive guide will help you understand everything you need to know about this life-changing immunotherapy.
Genprice
Scientific Publications
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cell Therapy: A Revolution in Cancer Treatment
What is CAR T-cell Therapy?
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is one of the most groundbreaking advancements in the field of cancer immunotherapy. This cutting-edge treatment harnesses the power of the body’s own immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells. Unlike traditional therapies such as chemotherapy or radiation, CAR T-cell therapy is a personalized approach that offers targeted treatment with long-lasting results. Read More.
How Does CAR T-cell Therapy Work?
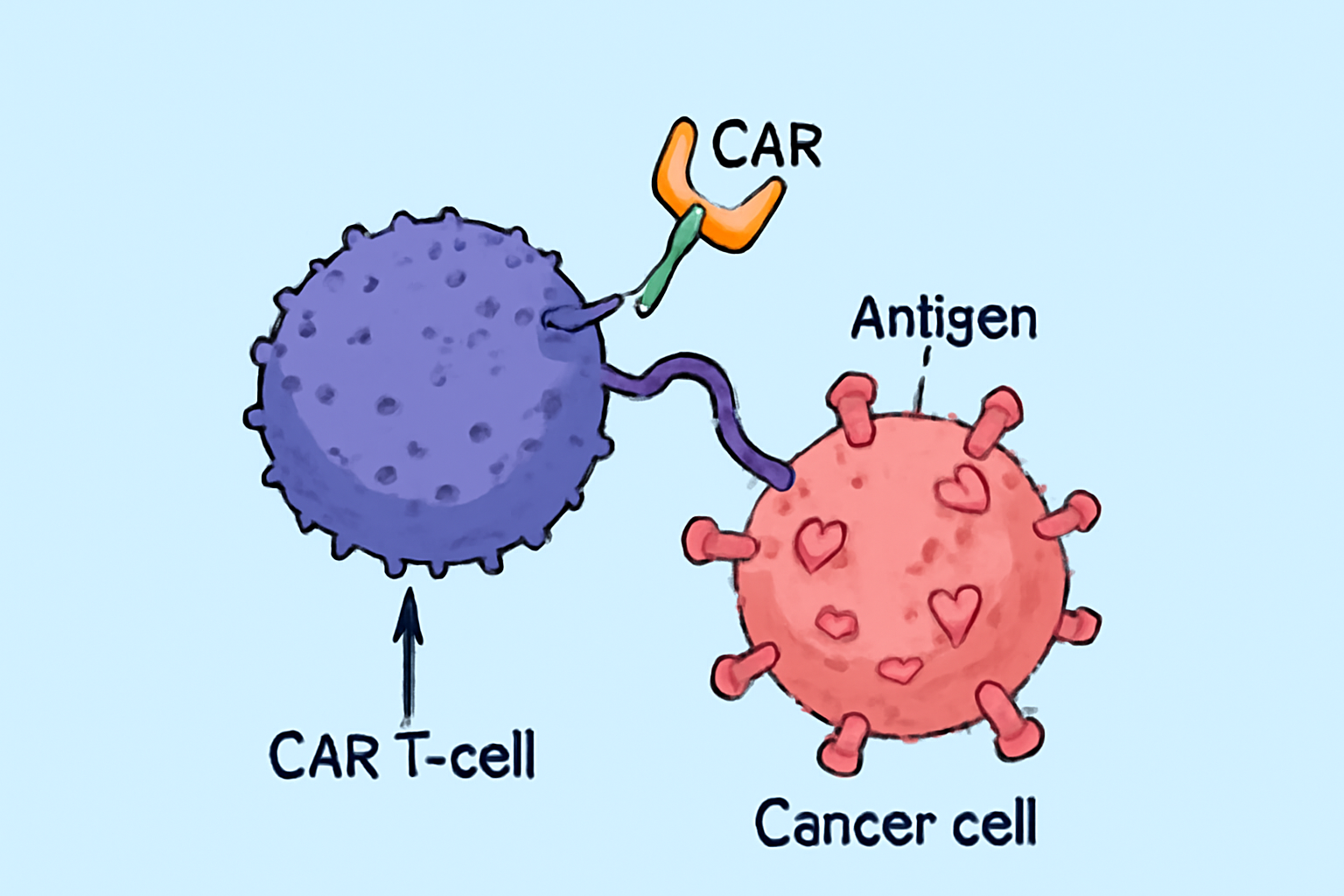
CAR T-cell therapy involves modifying a patient's own T cells—a type of white blood cell that plays a central role in immune defense. Scientists extract these T cells and genetically engineer them in the lab to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) on their surface. These CARs are synthetic proteins that allow the T cells to identify specific markers (antigens) on cancer cells.
Once these engineered T cells are infused back into the patient, they seek out and destroy cancer cells expressing the target antigen. The therapy essentially reprograms the immune system to become a cancer-fighting machine.
A Step-by-Step Overview of the CAR T-cell Therapy Process
- Leukapheresis: The patient’s blood is collected, and T cells are separated.
- T-cell Engineering: In a specialized laboratory, the T cells are modified using viral vectors to express CARs.
- Cell Expansion: The CAR T cells are grown in large numbers until there are millions ready for infusion.
- Lymphodepletion: Before infusion, patients typically undergo chemotherapy to reduce existing immune cells, creating space for CAR T cells.
- CAR T-cell Infusion: The modified cells are reintroduced into the patient’s bloodstream.
- Post-Treatment Monitoring: Patients are monitored for efficacy and potential side effects such as cytokine release syndrome (CRS) or neurological toxicity.
Indications: What Cancers Can Be Treated with CAR T-cell Therapy?
CAR T-cell therapy has shown remarkable success in treating blood cancers, particularly:
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
- Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL)
- Mantle Cell Lymphoma
- Multiple Myeloma
Ongoing research is expanding the scope of CAR T therapy to include solid tumors such as breast, lung, and pancreatic cancers, although challenges remain due to the complex tumor microenvironment and antigen heterogeneity.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
While CAR T-cell therapy is powerful, it’s not without risks. The most common adverse effects include:
- Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS): A systemic inflammatory response that can range from mild flu-like symptoms to life-threatening complications.
- Neurological Toxicities: Including confusion, seizures, or encephalopathy.
- B-cell Aplasia: Particularly in therapies targeting CD19, which may require immunoglobulin replacement.
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome: A metabolic complication resulting from rapid cancer cell destruction.
These side effects are generally manageable in experienced centers, with protocols in place for early detection and intervention.
The Future of CAR T-cell Therapy
The landscape of CAR T-cell therapy is rapidly evolving. Emerging innovations include:
- Allogeneic “off-the-shelf” CAR T cells: From healthy donors, eliminating the need for individualized manufacturing.
- Multi-specific CARs: Targeting multiple antigens simultaneously to reduce tumor escape.
- Armored CAR T cells: Engineered to secrete cytokines or resist immunosuppressive signals within tumors.
- Combination Therapies: Pairing CAR T cells with checkpoint inhibitors, vaccines, or chemotherapy.
Final Thoughts
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is redefining the frontiers of cancer treatment. It showcases the potential of genetic engineering and personalized medicine to deliver highly effective, long-lasting, and targeted therapies. While challenges remain, the progress so far has been nothing short of revolutionary.
Whether you're a patient, healthcare provider, researcher, or biotech professional, understanding CAR T-cell therapy is essential as it continues to shape the future of oncology and immunotherapy.
